One of the hidden gems at McMurdo, in terms of science experiments, is the COSRAY Neutron Detector. I had the opportunity to go inside the current COSRAY Building at McMurdo, led by technician James Roth.
More on COSRAY, from UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE BARTOL RESEARCH INSTITUTE NEUTRON MONITOR PROGRAM :
A neutron monitor is an instrument that measures the number of high-energy particles impacting Earth from space. For historical reasons these particles, mostly protons and helium nuclei, are called “cosmic rays.” Because the intensity of cosmic rays hitting Earth is not uniform, it is important to place neutron monitors at multiple locations in order to form a complete picture of cosmic rays in space. Bartol Research Institute currently operates 8 neutron monitors.

The McMurdo COSRAY building lies along the road connecting McMurdo to Scott Base

James Roth entering COSRAY

Inside, there’s a small living room and kitchen, computer room, and door into the main detector room.

The main COSRAY Detector Room. You can see various lab benches and desks, as well as the first bank of detectors in the middle.

COSRAY has been around since around 1960, and it looks like a bunch of the gear still there may be original..

James Roth removes insulation to show the ends of the neutron detectors.

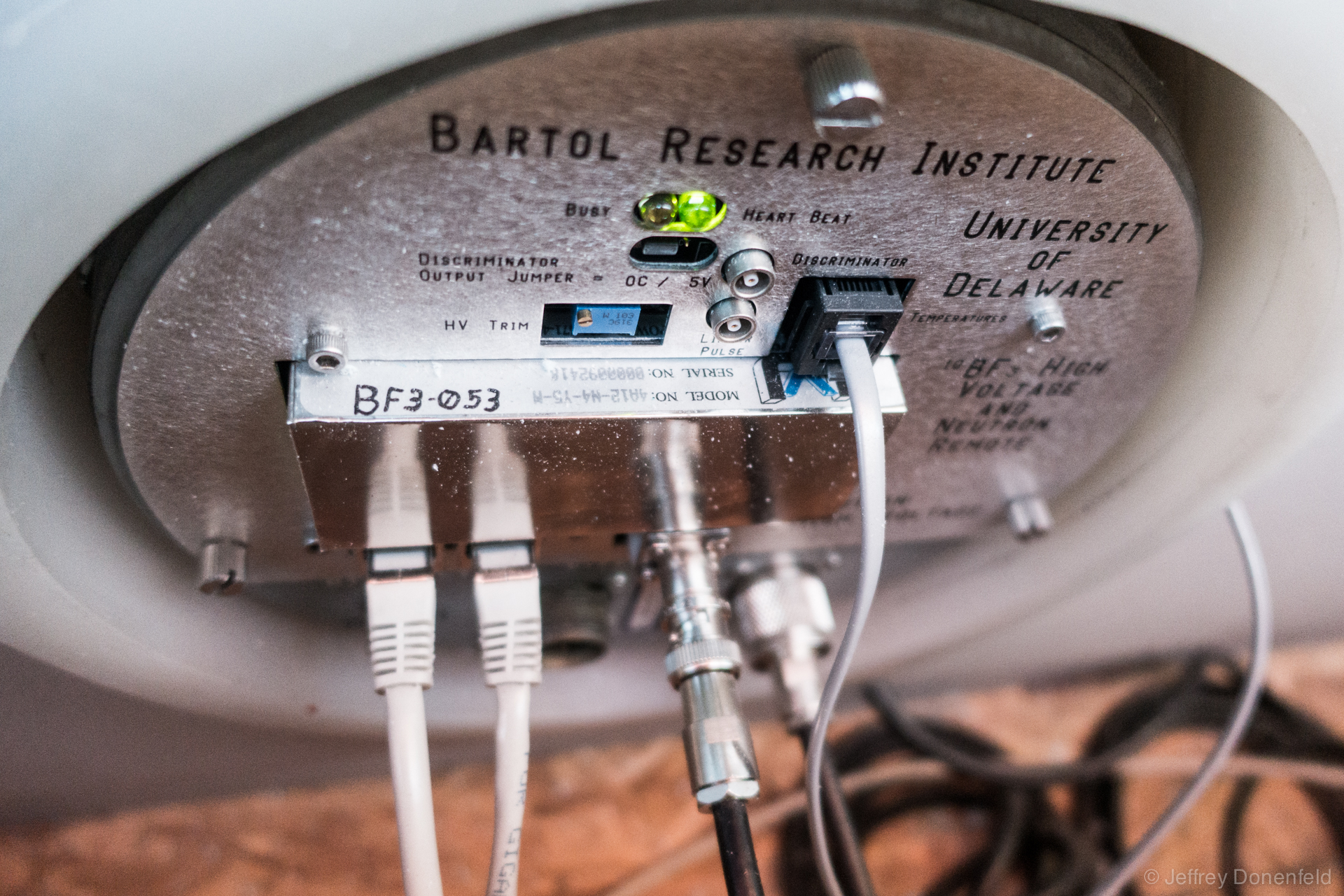
The electronics interface of the detector tube.

James Roth with the COSRAY bit bucket – these bits of paper were punched out of a long paper tape, used to store data before digital storage.

From https://neutronm.bartol.udel.edu/stations/mcmurdo.html : Inside the Cosmic Ray Lab. The neutron monitor is in three sections (white structures on floor) each containing six neutron detector tubes. Photo by L Shulman, 1999.

From https://neutronm.bartol.udel.edu/stations/mcmurdo.html : The cosmic ray lab at McMurdo Station, Ross Island, Antarctica. Behind the lab is the Ross Ice Shelf and, on the horizon, Black Island (left) and Mount Discovery (right). Open water at far right leads to McMurdo Sound. Photo by L Shulman, 1991.